Print quality troubleshooting guide
Improve the quality of your 3D-printed parts. A guide on how to fix the most common problems.
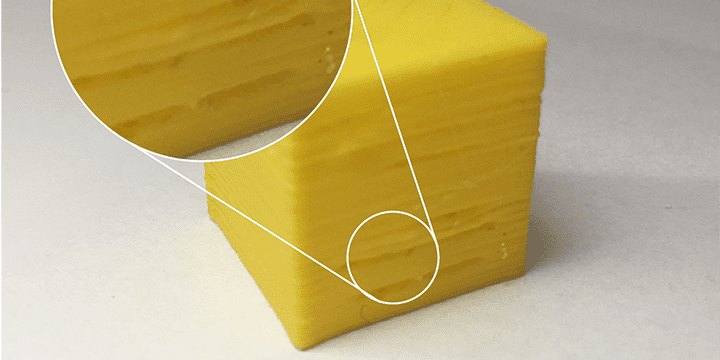
Layer separation on 3D printed part
Why do layers separate and what to do
In FDM 3D printing the parts are created layer by layer. If the layers do not bond properly, they will be separated or split resulting in a print that will be weak and easily break.
Too low temperature
If the printing material is not hot enough it will have difficulties to melt together with the layer beneath. Different materials require different temperature, for example PLA prints well at the temperature 180-210 degrees but ABS needs a higher temperature, around 220-235 degrees to create strong bonds between layers. The head temperature is too low, and should be increased. Check your temperature settings and try to increase the temperature by 10 degrees in REALvision Pro in the Printing settings/Expert level/Material Properties tab.
Filament entangled
The filament can sometimes get entangled, and the printer cannot extrude the filament. If this happens, try to disentangle the filament. Make sure it is rolling off properly from the spool.
Temperature fluctuations
If the temperature is fluctuating the extrusion can sometimes become inconsistent, or even stop completely. This will result in the layers not bonding strongly or at all together. For temperature fluctuations you should contact your reseller, and follow the instructions provided.
Printing settings in REALvision Pro
You can find the Printing Settings in REALvision Pro on the left panel as shown on the image on the left. The settings are available on three levels based on the users` experience with 3D printing: Basic, Advanced and Expert.
You can learn more in our Academy.
Too large layer height
The layer height is dependent on the nozzle, but in general it should be set to 20% smaller than the nozzle`s diameter. Most nozzles`diameter is between 0,3 – 0,5 mm. If the setting is incorrect the layers will not bond well together. Try to reduce the layer height in REALvision Pro in Printing settings/Expert level/Model tab.
You can also use a feature here called layer height division. This function automatically splits the layers into several thinner layers. It will also result in a more smooth surface but also in a longer printing time. You can find this option in the Printing settings/Expert level/Printing strategy/Layer height division.
Cooling settings
In case of certain materials, such as ABS and PEEK if the fan speed is set too high it can also cause layer separation. Decrease the fan speed in REALvision Pro in the Printing settings/Expert level/Material Properties.
A software program to fit your needs
If you want to get quality prints without doing 3D modeling, consider adding REALvision Pro to your 3D printer kit. We promise you easy-to-use 3D slicing software in the high-end printing industry. Suppose you are:
- A picky hobbyist with a cheap desktop 3D printer.
- Running a 3D printing service with flawless 3D prints.
- 3D printing metal parts for aerospace.
- 3D printing customizable prosthetics, implants, or casts in ABS plastic (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene).
- Rapid prototyping 3D models from design software.
- Need help with calibration or material profiles.
- Finding the best 3D printer for your application.
- Exploring manufacturing processes and technology to obtain zero-waste.
In that case, we have a software plan fitting your needs.
Did you know?
FDM printing comes from the abbreviation Fused Deposition Modeling and it is also known as Fused Filament Deposition (FFD) technology, and as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF). The spool of filament is the material used to build the 3D part by melting the plastic out of the nozzle of the 3D printer. All 3D printing filament starts out in pellet form – small granules of plastic. The filaments can be made of different types of plastic. The most commonly used plastics are PLA which is Polylactic Acid and ABS which stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. Both materials have favorable mechanical properties, ABS is well known for its impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity, and is also commonly used in injection molding besides additive manufacturing. PLA is known for its low melting point, high strength, low thermal expansion, good layer adhesion, and high heat resistance. It has also become a popular material due to it being economically produced from renewable resources (bioplastics).
The printer extrudes this filament line by line, layer by layer, by increasing the z-axis, and will build the 3D printed part.